New actions and recommendations announced at COP27 will make nature-based solutions a go-to option for fighting climate change and boost progress towards U.S. climate goals. The White House provided this fact sheet:
The Biden-Harris Administration at COP27 in Egypt released the Nature-Based Solutions Roadmap, an outline of strategic recommendations to put America on a path that will unlock the full potential of nature-based solutions to address climate change, nature loss, and inequity. This marks the first time the U.S. has developed a strategy to scale up nature-based solutions.
To demonstrate how the U.S. is already taking action, the Administration also announced new and recent interagency commitments aligned with the roadmap including: agency actions to ensure over $25 billion in infrastructure and climate funding can support nature-based solutions; a new guide for bringing the power of nature to maximize the value and resilience of military bases; and a new technical working group to better account for nature-based options in benefit cost analysis – a powerful tool for federal decisions.
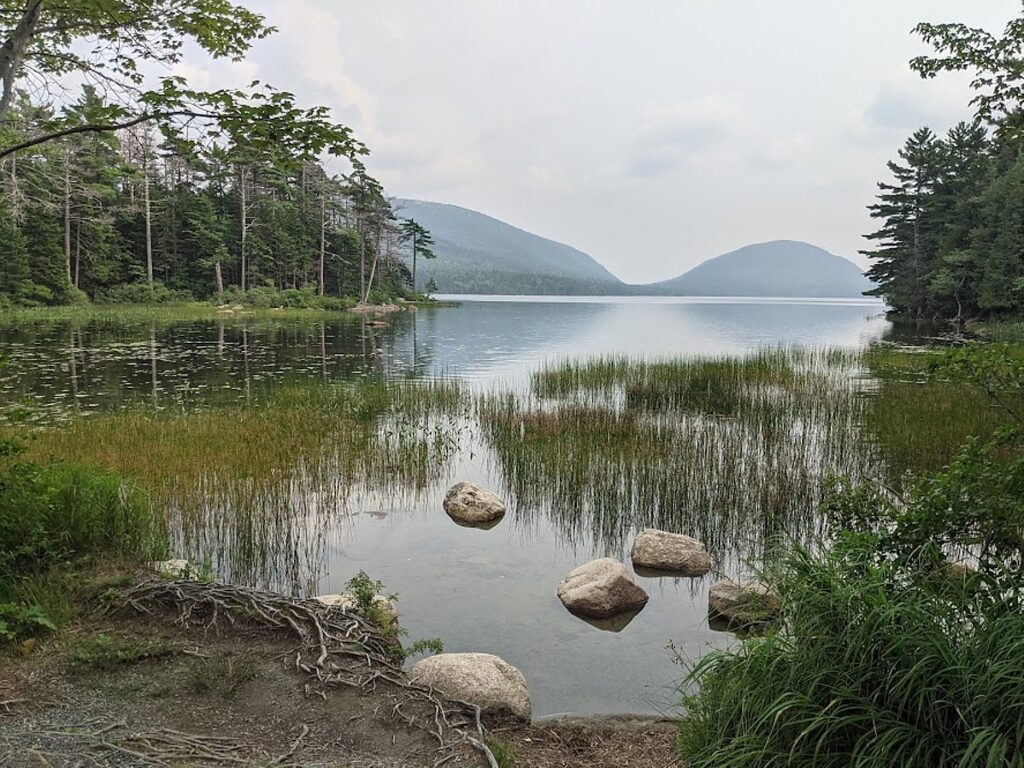
Nature-based solutions are actions to protect, sustainably manage, or restore natural or modified ecosystems as solutions to societal challenges, like fighting climate change. Examples include protection or conservation of natural areas, reforestation, restoration of marshes or other habitats, or sustainable management of farms, fisheries, or forests. These actions can increase resilience to threats like flooding and extreme heat, and can slow climate change by capturing and storing carbon dioxide. Nature-based solutions play a critical role in the economy, national security, human health, equity, and the fight against climate change.
John Podesta, Senior Advisor to the President for Clean Energy Innovation and Implementation, and chair of President Biden’s National Climate Task Force, unveiled the roadmap at the opening of the U.S. Center at United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change’s Conference of the Parties (COP27). Mr. Podesta encouraged other nations to join the U.S. by taking bold action to invest in nature and its many benefits.
On Earth Day 2022, President Biden issued Executive Order 14072, which recognizes the importance of forests and other nature-based solutions to tackle the climate crisis and strengthen communities and local economies. In the Executive Order, President Biden directed the Council on Environmental Quality, the Office of Science and Technology Policy, and the National Climate Advisor, in consultation with agencies, to identify key opportunities for greater deployment of nature-based solutions across the Federal government. The Roadmap submitted to the National Climate Task Force today calls on expanding the use of nature-based solutions and outlines five strategic areas of focus for the federal government: (1) updating policies, (2) unlocking funding, (3) leading with federal facilities and assets, (4) training the nature-based solutions workforce, and (5) prioritizing research, innovation, knowledge, and adaptive learning that will advance nature-based solutions.
This work builds on President Biden’s climate leadership. The Administration is already advancing nature-based solutions in support of the President’s commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions 50-52% below 2005 levels in 2030, to conserve at least 30% of U.S. lands and waters by 2030, and to increase community resilience to extreme weather and other climate impacts. The new Nature Based Solutions Roadmap will help the Administration seize additional opportunities; key recommendations and related new and recent agency commitments are below.
The Biden-Harris Administration also released a companion resource guide with examples of nature-based climate solutions and over 150 resources to spur action. The Nature-Based Solutions Resource Guide: Compendium of Federal Examples, Guidance, Resource Documents, Tools and Technical Assistance is available here.
NATURE-BASED SOLUTIONS ROADMAP: FIVE STRATEGIC AREAS FOR ACTION
- Update Policies to Accelerate Nature-Based Solutions
The roadmap recommends that agencies update federal policies and guidance, making it easier to consider and adopt nature-based solutions. Major areas for advancement include policies and guidance for federal planning, permitting, cost-sharing, risk management, and benefit cost analysis. Aligned Administration actions include:
- Guidance on valuing nature: Current federal policies and guidance on accounting and analysis can under-value nature-based solutions. The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is reviewing central guidance on benefit cost analysis (Circulars A-4 and A-94) to help federal agencies more fully account for the value of nature in regulatory and funding decisions. Today, the White House is standing up a new technical working group on Frontiers of Benefit Cost Analysis to support agencies in benefit cost analysis for nature-based solutions and other analysis needs. This is coupled with the developing National Strategy for a system of natural capital accounts, which will place nature on the nation’s balance sheet and allow regular tracking of the economic benefits that investments in nature-based solutions provide.
- Nature-based solutions in floodplain management: The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is revising its floodplain management requirements to require consideration of nature-based solutions as alternatives for all projects that have the potential to affect floodplains or wetlands. This action is in response to Executive Order 13690, which established the Federal Flood Risk Management Standard that requires federal agencies to amend their floodplain policies to consider the use of nature-based solutions. Interim program policies are underway.
- Unlock Funding for Nature-Based Solutions
Federal funding for domestic and international projects can provide a strong lever to increase deployment of nature-based solutions. The roadmap recommends that Federal agencies do more to prioritize nature-based solutions in funding decisions; increase and ease access to this funding; and catalyze private investment. Actions by the Administration to unlock funding include:
- Supporting nature-based solutions in hazard mitigation: FEMA’s Building Resilient Infrastructure and Communities (BRIC) grant program already prioritizes nature-based solutions in its project scoring criteria. Last month, FEMA announced a new effort that will reduce the burden of applying for BRIC funding for disadvantaged communities, and that may make it easier for projects with nature-based solutions to access funding. This effort reduced the discount rate from 7% to 3% for these communities on some projects in FY 2022.
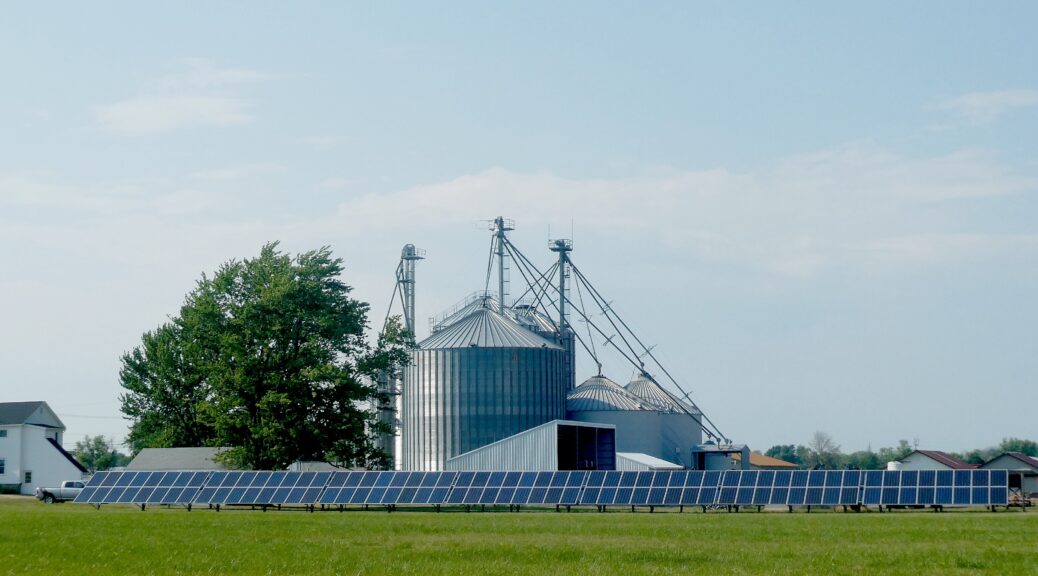
- Combining solar energy and nature-based solutions: The Department of Energy Solar Energy Technology Office (SETO) is investing in combined development of ground mounted solar systems and pollinator habitat. In fiscal year 2022, SETO selected projects worth $14 million for Deploying Solar with Wildlife and Ecosystem Services Benefits, developing innovative strategies that maximize benefits and minimize impacts to wildlife and ecosystems from solar energy infrastructure.
- Lead with Federal Facilities and Assets
The roadmap recommends that federal agencies expand their use of nature-based solutions in the design, retrofitting, and management of federal facilities and embed these solutions in management of natural assets through improved planning, co-management, and co-stewardship. Given the scale of federal assets, expanding deployment of nature-based solutions would have direct climate and conservation benefits and send a strong signal to others. Administration actions include:
- Guide on nature-based solutions for military installations: The Department of Defense is developing a guide on nature-based solutions for Military Installation natural resources management planning. The guide will provide military installation planners and managers with current and actionable information on the appropriate use of nature-based solutions; the current state of science and observed performance reliability; and other considerations regarding design, cost and benefits, implementation, and operations and maintenance. Preliminary guidance will be published in March 2023, with the full technical guide expected by March 2024.
- Nature-based solutions for energy, the economy and national security: In October, 2022, the Department of Energy launched Sustainable Climate-Ready Sites (SCRS), a site performance rating system. The program challenges DOE sites to apply innovative nature-based solutions as they manage 2.4 million acres of land and carry out their missions. SCRS performance criteria include environmental justice and cultural resource protection, emphasizing collaboration and engagement with communities and Tribal nations. Annual leadership awards will be given to personnel at participating sites that achieve top SCRS category scores.
- Train the Nature-Based Solutions Workforce
We need a diverse, equitable workforce skilled in building nature-based solutions. To reach this goal, the roadmap recommends that agencies expand educational and workforce training offerings related to nature-based solutions to support good jobs in federal agencies and the private sector. These needs apply across a wide range of skills including engineering, law, finance, ecology, accounting, economics, community planning and maintenance for nature-based solutions. Administration actions include:
- Growing awareness of how nature-based solutions benefit households: The Department of the Treasury’s Financial Literacy Education Commission (FLEC) is producing a series of reports entitled How Climate Challenges American Household Finances. One report in the series will address housing, and FLEC will include ways that nature-based solutions can provide benefits to households through housing and landscaping options. The report will be released in 2023.
- Prioritize Research, Innovation, Knowledge, and Adaptive Learning
As the world changes, we must continually innovate and fill gaps in our understanding. The roadmap recommends that federal agencies advance research and innovation in all sectors to fully reveal the scale of the opportunity that nature-based solutions provide, and incentivize continual learning about how and where nature-based solutions work best. Administration actions include:
- Synthesizing what we know about nature-based solutions effectiveness: Nature-based solutions have been evaluated in different ways by different experts and sectors, making it difficult to see the big picture of what we now about where and how these solutions provide benefits. Today, the U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP) is announcing a study to synthesize this multi-disciplinary evidence base, and evaluate the effectiveness of nature-based solutions for climate mitigation, adaptation and other benefits. An initial database of evaluations will be made public in 2023 and the analysis will be available by 2024.
- National summit on measuring nature-based solutions: The USACE will host a National Summit on Measuring What Matters at the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine in Washington D.C. on November 30, 2022. At the public Summit, the USACE Engineering with Nature Program will share the results of a two-year project focused on approaches for advancing comprehensive benefit evaluation for nature-based solutions and other projects.
BUILDING ON THE BIPARTISAN INFRASTRUCTURE LAW AND INFLATION REDUCTION ACT
The roadmap and aligned actions build on major investments made through President Biden’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and Inflation Reduction Act. These laws made unprecedented investments in nature-based solutions, placing forests, agricultural lands and coastal wetlands front and center in the climate fight. For example, $20 billion is directed to farmers, ranchers, and private forest owners working to increase carbon storage and reduce emissions. Another $5 billion is for forest management actions that can reduce wildfire risk, store carbon, and cool communities. These laws also weave nature into infrastructure investments. Over $8.7 billion will build climate resilience into transportation systems from the ground up. Another $8.6 billion will restore and conserve coastal habitats, investments that will buffer communities from storms and boost local economies. Several agencies are acting to leverage recent laws and appropriations towards nature-based solutions, including:
- Increasing carbon stored in wetlands and grasslands: The Inflation Reduction Act provides additional funding for the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resource Conservation Service (NRCS) conservation programs, including the Agricultural Conservation Easement Program (ACEP). In FY23, this funding will be targeted to improve climate and environmental outcomes. The programs will prioritize conservation and restoration of carbon rich wetlands and conservation of grasslands that are at risk of losing carbon and habitat through conversion to more intensive agriculture.
- Promote resilient housing: The Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), through the new Green Resilient Retrofit Program, is administering $837.5 million in grant funds and $4 billion in loan authority provided through the Inflation Reduction Act. This program provides grants that include nature-based solutions to improve energy efficiency, water efficiency, and climate resilience. HUD will ensure the program promotes nature-based solutions as effective investments to improve a properties’ climate resilience. HUD will encourage owners to implement the nature-based solution recommendations, where appropriate and feasible. Additional technical assistance will be offered with this program to aid communities in exploring nature-based solutions.
- Protecting watersheds and communities with nature-based solutions: The Bipartisan Infrastructure Law includes more than $23 billion in supplemental funds to EPA’s Clean Water and Drinking Water State Revolving Funds and nearly $1.9 billion to EPA’s place-base Geographic, National Estuary and Gulf Hypoxia programs. In its March 2022 Bipartisan Infrastructure Law SRF Implementation Memo, EPA emphasized the importance and eligibility of nature-based infrastructure, and encouraged states and communities to make full use of the SRF Green Project Reserve, which supports nature-based solutions and other environmentally innovative activities. EPA’s implementation of its National Estuary, Geographic, and Gulf Hypoxia programs also prioritizes use of nature-based solutions, where applicable, to restore coastal and riparian ecosystems and protect the communities that depend on them.
- Coordinating access to funds that reduce floods and benefit wildlife: The White House Infrastructure Implementation Task Force is advancing an effort to simplify access to new Bipartisan Infrastructure Law funds that aim to reduce the risk of flooding, improve habitat connectivity for fish and wildlife, and improve public safety. The Department of the Interior’s Fish and Wildlife Service, Department of Transportation, U.S. Department of Agriculture, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) are coordinating to facilitate access to these opportunities and ensure efficient use of federal funds.
- Advancing Coastal Resilience with Natural Infrastructure Projects: Through its Climate Ready Coasts Initiative, the Department of Commerce’s NOAA is helping coastal communities by investing in high-impact natural infrastructure projects that build economic and environmental resilience, create jobs, store carbon and restore habitat. The $1.5 billion in Bipartisan Infrastructure Law funds will be supplemented by future Inflation Reduction Act funding opportunities.
DRIVING GLOBAL ACTION
President Biden is committed to unlocking the full potential of nature-based solutions for achieving climate goals and combatting nature loss, especially for communities that are disproportionately impacted by climate change and environmental injustices. By announcing this roadmap and actions at the UNFCCC COP27, we recognize the need for global action to confront these triple crises and look forward to announcing additional actions during the upcoming Convention on Biological Diversity COP15. We invite partners, communities, and other nations to join the Biden-Harris Administration in taking aggressive action to advance nature-based solutions as powerful tools that the world needs now.