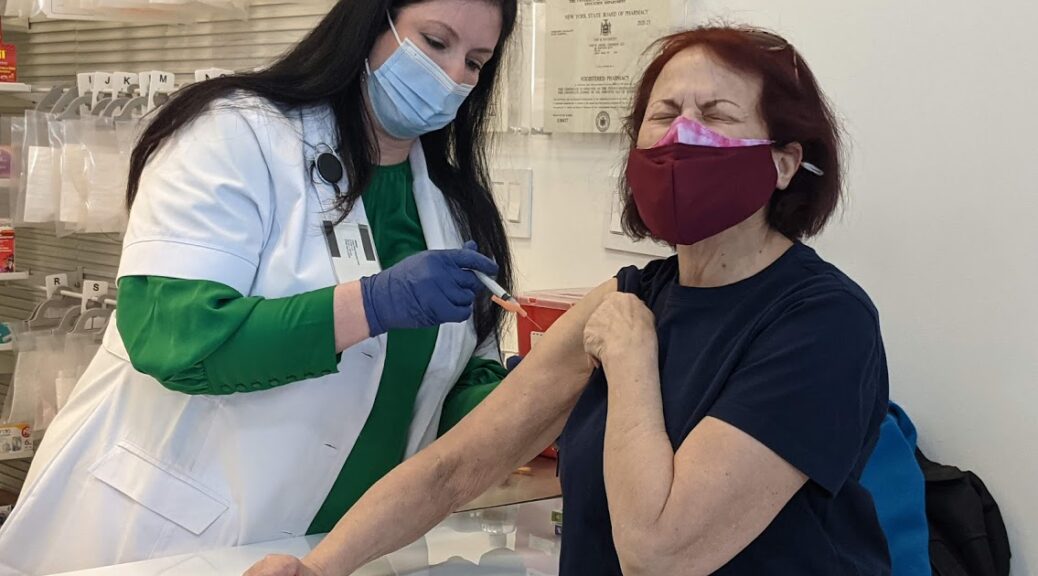
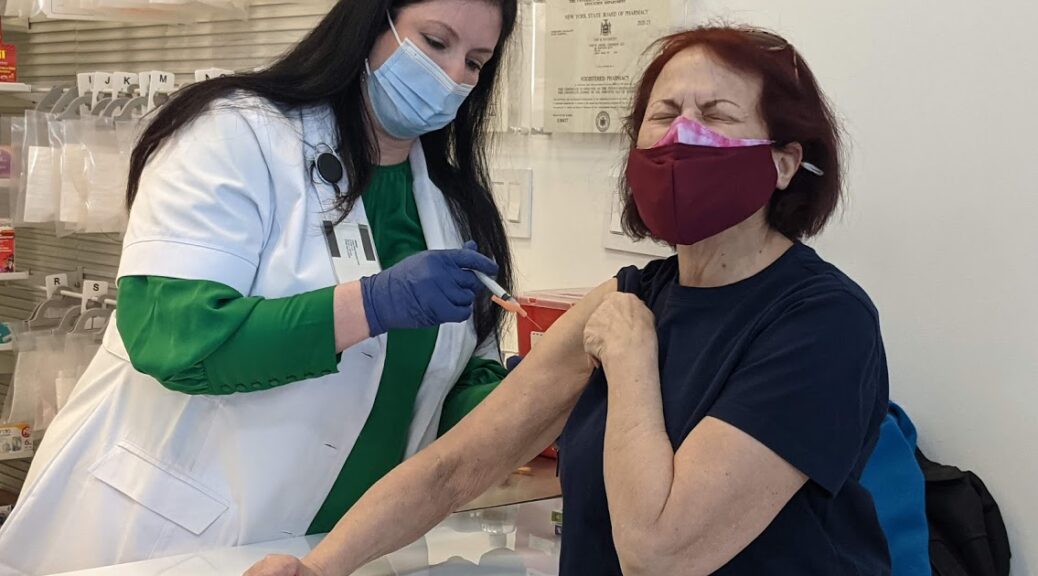
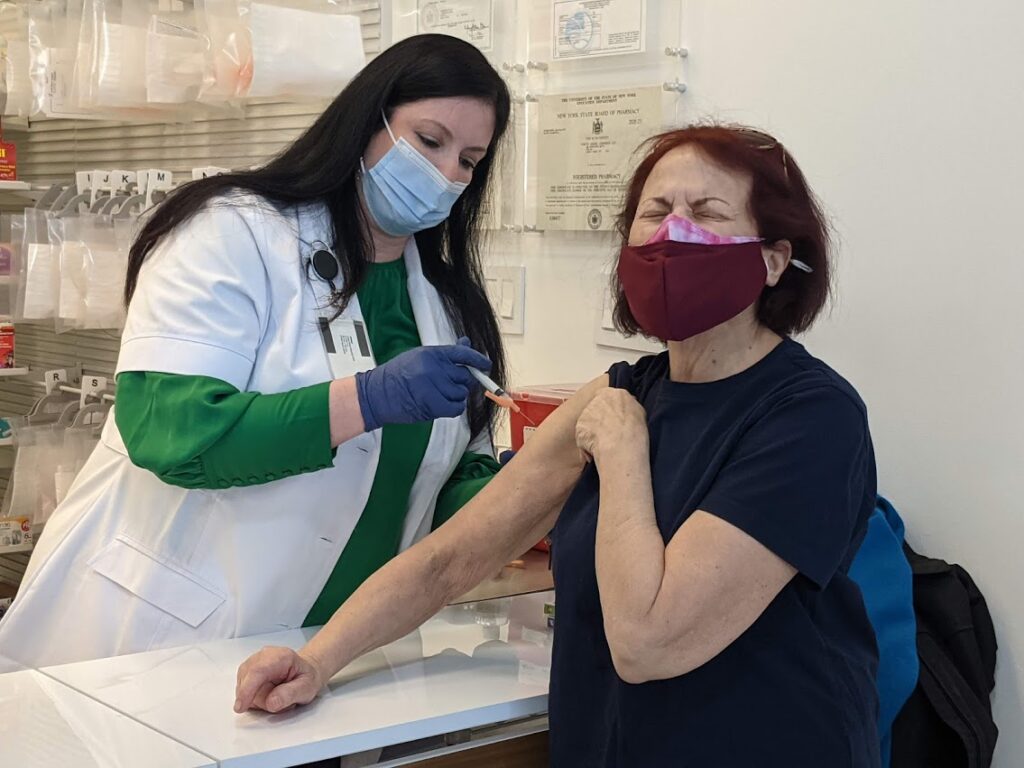
Driven by President Biden’s comprehensive COVID-19 strategy, including a historic vaccination program that has gotten 220 million Americans fully vaccinated, over 100 million people a booster shot, and made vaccines free, widely available and convenient—daily COVID-19 deaths are down 90 percent since he took office.
COVID-19 vaccines remain the single-most important tool that we have to protect people against COVID-19 and its most serious outcomes. Next week, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) will consider whether to authorize and recommend the first COVID-19 vaccines for kids under the age of 5. If FDA authorizes and CDC recommends one or both of the COVID-19 vaccines for this age group, it would be a historic milestone in the nation’s fight against the virus—and would mean nearly every American is eligible for the protection that vaccination provides.
The Biden Administration announced an operational plan that will ensure that vaccines—now authorized by FDA and recommended by CDC—are readily available for our youngest kids and that we continue the critical work of ensuring that all families know the benefits of getting their children vaccinated against COVID-19.
The Administration’s vaccination program for America’s youngest children will focus on addressing the specific needs of this age group and their families—recognizing that many parents and guardians will choose to get their kids vaccinated through their pediatrician or primary care doctor. As always, state and local governments, health care providers, federal pharmacy partners, national and community-based organizations, and other entities will be critical to the success of this historic, nationwide effort. And, the Administration will continue to work with trusted messengers, including pediatricians, to make a concerted effort to ensure that all families have answers to their questions and know about the importance of getting their children vaccinated.
As the FDA and CDC conduct their independent review processes, the Biden Administration is planning for all scenarios, including for the first vaccinations to start as early as the week of June 20th—with the program ramping up over time as more doses are delivered and more appointments become available.
For months, the Administration has been working with a range of stakeholders to get ready. The Administration has made 10 million vaccine doses available for states, Tribes, territories, community health centers, federal pharmacy partners, and others to pre-order. If the FDA authorizes a vaccine, the Administration will immediately begin shipping doses across the country—and will launch an effort to ensure that parents can get their youngest children vaccinated easily. 85 percent of children under the age of five live within five miles of a potential vaccination site.
The Biden Administration’s plan includes:
Securing vaccine supply for our nation’s children. The Administration has procured a significant supply of vaccines for this age group, with 10 million doses available initially and millions more available in the coming weeks. To ensure that we are able to reach a broad range of pediatric providers—including those in smaller practices and in rural settings—vaccines will be available in package sizes of 100 doses and will come with all of the supplies that health care providers need to serve younger kids, including small needles.
Making vaccinations available in convenient places parents and families know and trust. Working with states, localities, Tribes and territories, the Administration will make vaccinations for our nation’s youngest children widely available at thousands of trusted, accessible sites across the country—with 85 percent of children under the age of five living within five miles of a potential vaccination site. Vaccinations will be available at pediatricians’ and other doctors’ offices, community health centers, rural health clinics, children’s hospitals, public health clinics, local pharmacies, and other community-based organizations. The Administration will also work with state and local public health departments and others to ensure that every child—including those who may not have a pediatrician or primary care provider—has access to the vaccine. And, the Administration will work with states and other entities to make vaccinations available at convenient hours for children, parents and their guardians—including after school and evenings, and on weekends.
- Pediatricians and primary care providers: The Administration will make vaccinations available at thousands of pediatric and primary care sites across the country. Pediatricians continue to be one of the most trusted sources of information about COVID-19 for parents and will play a critical role in the nationwide effort to get our youngest children vaccinated—as they are the most common, trusted location for routine childhood vaccines. More than three in four children under the age of five receive their flu vaccine in a doctor’s office. Well-patient visits are also an opportunity for pediatric providers to conduct recommended screenings and provide counseling. The Administration is working hand-in-hand with states, localities, Tribes, and territories to prioritize these providers and ensure that they have the supply, resources, and support they need. The Administration will also continue to make vaccines available directly to health centers and rural health clinics, who together serve more than 2.2 million children under five nationwide.
- Children’s hospitals and health systems: The Administration will make vaccinations available at more than 100 children’s hospitals and health systems nationwide. Children’s hospitals play an essential role in our efforts to ensure access for our nation’s highest-risk kids, including those with obesity, diabetes, asthma or immunosuppression. Through the Administration’s partnership with the Children’s Hospital Association, more than 120 children’s hospitals across 47 states and D.C. will provide pediatric vaccinations across their health care systems and in trusted community sites.
- State and local public health clinics and sites: The Administration will build on its longstanding work with state and local health departments across the country to ensure that we are reaching those hardest-to-reach, including families who may not have regular access to a pediatrician, through public health clinics. The Administration will make available federal funding to support states as they stand up and operate these clinics, and will work hand-in-hand with states to maximize vaccination coverage and availability, particularly in the hardest-hit, highest-risk communities.
- Local pharmacies: The Administration will make vaccinations for children available at thousands of local pharmacies nationwide through the federal pharmacy program. Participating pharmacies will offer vaccinations for this age group in a more limited set of locations, in many cases at clinics staffed by health care providers with primary care experience. And pharmacies will offer convenient hours and advanced scheduling to best meet the needs of parents and communities.
Leveraging federal programs to reach parents and families with information and advance equity. As with prior vaccination efforts, the Administration will leverage existing federal programs and capabilities to ensure that we are reaching parents and families with the information they need. And, as always, the Administration will remain laser-focused on equity and making sure that we reach those hardest-hit and most at-risk communities.
- Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) Program: In addition to other U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) programs, the Administration will engage families through the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) program, which serves over 6 million people, including almost half of all infants born in the United States. A longstanding partner to immunization programs, WIC settings across the country will be provided with tailored resources for talking to families about the COVID-19 vaccine and will continue providing families with referrals to vaccination providers, including those co-located with WIC settings.
- Head Start Program: Through the Administration for Children and Families at the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Administration will work with Head Start grantees to get critical vaccination information to the approximately 1 million families they serve. Head Start has always played a crucial role in improving health outcomes for families, and COVID-19 is no different. The Administration will support training and resources for grantees to learn about vaccines for kids under five and how grantees can talk to families about them, and it will ensure that any Head Start location is ready and able to provide vaccinations to its community gets the help it needs.
- Maternal, Infant, and Early Childhood Home Visiting (MIECHV) Program: The Administration will engage families through HHS’ Maternal, Infant, and Early Childhood Home Visiting (MIECHV) Program, which each year reaches more than 140,000 parents and young children across the country that are at risk for poor maternal and child health outcomes. MIECHV home visitors will leverage these established relationships to help families learn more about COVID-19 and the safety, efficacy, and benefits of COVID-19 vaccines and, upon request, will refer families to local vaccination sites.
- Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) programs: The Administration will launch an effort to reach more than 800,000 children age five and under supported by HUD programs, including children in households that receive housing-choice vouchers and children living in public housing and Section 8 housing. Building on successful campaigns with children in other age groups, these efforts will include education events and on-site vaccination clinics near HUD-supported housing where appropriate, in coordination with other vaccination locations in the community.
- Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP): The Center for Medicaid & Medicare Services (CMS) will take steps to support and push the message about the importance of vaccinating the millions of children under 5 who are enrolled in Medicaid and CHIP. This outreach will involve engaging states, local jurisdictions, and stakeholders to get the latest information on vaccines for this age group to Medicaid beneficiaries and their families. This effort builds on the work that CMS has already done to require state Medicaid programs to pay health care providers for providing counseling visits to parents and guardians about the importance of kids’ vaccination—giving families the support they need to engage with trusted community providers.
Supporting education and engagement efforts to build trust among parents and families. While many parents are eager to vaccinate their youngest children, others have questions. To ensure that parents and families have answers to their questions and information from sources that they trust, HHS will work with a broad range of national organizations to launch a national public education campaign that reaches parents, guardians, and families with facts and information that they need to make informed choices for both their youngest and their older children.
- The HHS COVID-19 Community Corps will reach parents and families about vaccinations for kids under the age of five. Launched last April to empower people and organizations to build vaccine confidence in their communities, the Community Corps now has over 17,000 members, including health care, faith, rural, sports, and youth organizations. The ‘HHS We Can Do This’ campaign will provide a pediatric COVID-19 vaccination toolkit—in both English and Spanish—to trusted messengers, health care providers, and state and local organizations so they can reach people where they are in-person and online. HHS will also provide additional materials for stakeholders, including a superhero-themed toolkit with creative resources for hospitals and pediatricians. And, pending FDA authorization and CDC recommendation, the Administration also plans to release a new public service announcement (PSA) letting parents of children 6 months and older know that the new COVID-19 vaccines are available and offer one more way to keep their children safe. The PSA, filmed in both English and Spanish, will be distributed broadly to local television and radio networks, and would air in early July.
- American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), two leading medical, will provide a “Speaker’s Bureau” of pediatricians and family doctors who will lend their trusted voices to raise awareness, answer common questions among parents, and encourage vaccine confidence through community events, vaccine and health fairs, and other key opportunities to reach parents. AAP and AAFP will also work with HHS to co-brand a toolkit of resources geared toward pediatricians and primary care doctors, providing these and other health care providers the information and materials they need to support vaccine confidence among their patients and parents.
- Association of Children’s Museums (ACM), a champion for children’s museums with more than 460 members in 50 states and 19 countries, will work with local member museums to: host vaccine pop-up clinics; provide in-person and virtual events including information sessions, community forums, and other events featuring museum leaders and medical experts to answer parent questions; display a museum exhibit providing educational information about vaccination in English and Spanish; and amplify digital and social content to reach families.
- The National Diaper Bank Network, a nationwide organization with more than 200 member diaper bank programs that distributed over 68 million diapers last year, will distribute educational material to parents and caregivers through member diaper banks, packing fact sheets, postcards, and other materials in diaper boxes, sharing resources with local agency partners, and hosting virtual and in-person events with pediatricians and other trusted messengers.
- The American Library Association (ALA) will provide resources to assist the nation’s 17,000 public libraries in providing trusted vaccine information to parents and guardians. ALA will conduct a national webinar for librarians and staff featuring a pediatrician from AAP and other trusted messengers to provide information to public librarians and staff on how they can support vaccine education and outreach, share resources through children’s programming, and host in-person events and vaccine pop-up clinics to promote vaccines in their communities. Public libraries have played an important role in the pandemic by equipping their communities with trusted information, supplies like masks and COVID-19 tests, and hosting pop-up vaccine clinics.
- The National Parent Teacher Association (PTA) has been hosting dozens of vaccine pop-up clinics to reach parents, teachers, and school staff. The National PTA will continue to engage parents of school-aged children, as well as parents of younger children, by hosting a national symposium for local PTA leaders and affiliates featuring a pediatrician from AAP and other trusted messengers; hosting vaccine pop-up clinics in key geographic markets to reach parents of both school-aged and younger children; and hosting virtual events to reach parents and empower community leaders to act as trusted messengers and amplify vaccine information.
- The National Association of Community Health Centers (NACHC), the leading association for community health centers, will provide culturally appropriate and evidence-based training to empower community health centers to act as trusted messengers with parents of school-aged and younger children and other patients in their communities. NACHC will also host virtual events, including webinars, trainings, and podcasts to aid in the dissemination of campaign materials and messaging about the importance of vaccinations for young children, and how community health workers can play a key role in reaching parents with trusted messaging.
- Latino community-focused organizations, including the League of United Latin American Citizens (LULAC), the largest and oldest Hispanic serving organization in the US with over 1,000 LULAC Councils, will hold in-person and virtual educational events for parents and caregivers and will design and distribute bilingual, culturally relevant resources (printed and digital) to community members and partner organizations.
- Black community-focused organizations, including the W. Montague Cobb Health Institute, a consortium of scholars working toward the elimination of racial and ethnic health disparities within the National Medical Association, will host “Stay Well Health Fairs and Vaccine Clinics,” an ongoing series of health fairs offering free vaccines, educational materials, health screenings, and pediatric roundtables featuring subject matter experts. The Women’s Missionary Society Foundation, with 800,000 members across the African Methodist Episcopal (AME) Church’s boundaries, will host “family fun day” vaccine events reaching Black families and will collaborate with AME Church daycares and pre-schools to share information and messaging about pediatric vaccines.
- Asian American, Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander community-focused organizations, including the Asian Community Development Council, The Progressive Vietnamese American Organization, Ethnic Minorities of Burma Advocacy and Resource Center, Chinese Community Center, Filipino Family Health Initiative, and Thai Community Development Center will: engage with local communities in Chinese, Korean, Vietnamese, Tagalog and other languages where possible through in-person engagement, phone banking, social media and written resources; reach families through WIC Market Match, which serves parents with small children who are on WIC; and host weekly vaccine clinics and vaccine education classes and events.
- Native American community organizations, including Native Roots Radio, a leading radio station for Native Americans to discuss local, regional, and national Native American news and events will conduct virtual conversations including physicians, community advocates, and Tribal leadership speaking on the COVID-19 pandemic including vaccinations for children, boosters, mental health and long COVID; and the USDA Food Distribution Program on Indian Reservations in partnership with the Great Plains Tribal Leaders Health Board will distribute educational materials to food distribution centers to be packaged in food boxes promoting vaccinations that are regionally and culturally tailored to Native American audiences.
What to Expect, a platform of over 20 million moms, will author a blog series featuring doctors and other trusted experts answering questions about pediatric COVID-19 vaccines, and how moms, expecting moms, and all parents can get the information they need to get themselves and their children vaccinated; author new articles dispelling myths about the COVID-19 vaccine and children; and create and amplify new What to Expect social media content, reaching moms where they are and fighting vaccine misinformation across all platforms.