While Trump, Elon Musk (the unelected but richest man in the world and Trump’s puppeteer) and the House Republicans are salivating over the prospect of shutting down the government to make sure Biden’s transformative, historic administration ends with suffering of the American people – even stopping the $100 billion in disaster aid – President Biden continues to work feverishly to effect as much positive, sustainable change as possible. This included stepping in to avert a nationwide Teamsters strike at the nation’s biggest ports, rebuilding a bridge over I-95 in Philadelphia and reopening the Port of Baltimore in a matter of weeks, not years, after a catastrophic accident collapsed the Key Bridge, and addressing a series of rail accidents. His historic, landmark Bipartisan Infrastructure Act has already greenlit some 63,000 projects across the nation.
Biden’s achievements in standing up the supply chain so ravaged by the coronavirus epidemic is why the United States never suffered the level of inflation as other countries – as much as people have complained about high grocery prices (apparently not factoring in record profits and price gouging of food suppliers) – and produced sustainable economic growth (from the bottom up and the middle out) that is the envy of the world.
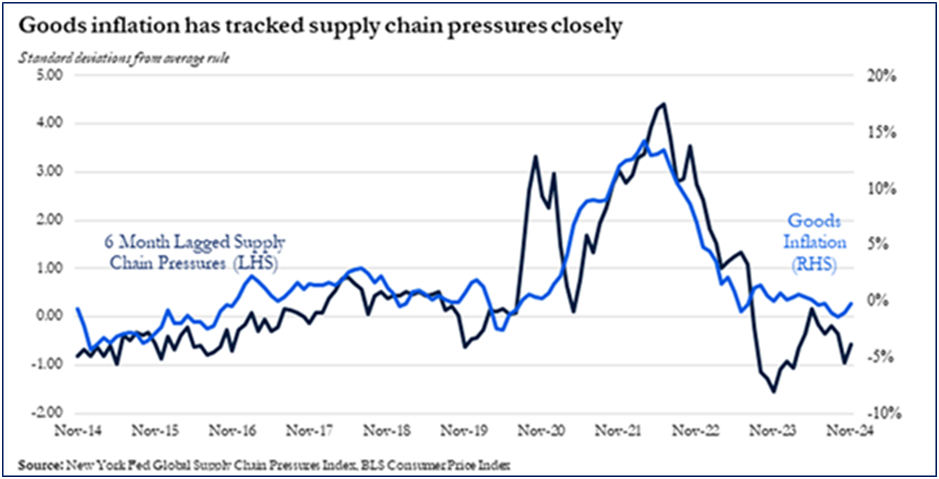
Here is a fact sheet, provided by the White House, on what the Biden Administration is doing to secure supply chains in order to keep grocery prices from spiraling as after the coronavirus pandemic’s disruption. Trump’s proposed tariffs and plans for mass deportation of undocumented migrants promise to trigger price spikes in groceries again.- Karen Rubin/news-photos-features.com
Upon taking office in 2021, President Biden and his Administration immediately got to work addressing the shocks that were roiling global supply chains and moved swiftly to secure key industries for America’s economy and national security. Everything in our lives—the food we eat, the medicines in our hospitals, the energy that powers our homes, the computer chips in our devices—relies on supply chains, and the disruptions sparked by the COVID-19 pandemic and Russia’s war on Ukraine showed what happens when they are neglected for decades.
Four years later, America’s supply chains are stronger and more resilient. Working hand in hand with industry and all stakeholders, this Administration has cleared bottlenecks, increased investments in critical sectors, and shored up the transportation sector that move the goods that Americans rely on. Ocean shipping prices have fallen more than 70 percent from their peak, and today fewer than 20 containerships are waiting to dock at U.S. ports, compared to over 150 backed up during the peak of congestion. That progress has made supply chains more reliable for businesses and lowered inflation for the goods that families buy every day.
The Biden-Harris Administration released the first-ever Quadrennial Supply Chain Review, a formal assessment of four years of strengthening America’s critical supply chains, and announcing additional actions to support American businesses and consumers.
Progress to Date
The Quadrennial Supply Chain Review assesses the progress made over the past four years to bolster the resilience of our most critical supply chains. This strategic approach has included:
- Responding to disruption. The Administration quickly set to work to develop new government tools and capacity to respond to disruptions, both active ones when it took office, and new ones that have occurred since. The President’s Supply Chain Disruptions Task Force (SCDTF) has effectively coordinated federal authorities and resources and also established a process to work with state and local authorities and the private sector in real time. This work has helped improved the flow of goods into and around the United States during disruptions—getting products critical to American families moving again through ports and to shelves.
- Investing in infrastructure and manufacturing and lowering costs. Over the past four years, the Biden-Harris Administration has taken a made historic investments to strengthen our industrial bases and lower costs. U.S. Government investment has helped catalyze over $1 trillion in private-sector announced investments since January 2021. These investments are supporting the construction of new factories and creating manufacturing jobs across the country.
- Responding to non-market policies and practices. On a level playing field, American businesses and workers can compete and win. However, our strategic competitors are continuing to engage in non-market policies and practices (NMPP) that undercut our collective resilience—directing their systems to target key industries for dominance by using excessive state subsidies and other forms of state support to dominate critical industries. As part of the Quadrennial Supply Chain Review process, the Biden-Harris Administration has developed a strategy to address NMPP, recognizing the need for early, comprehensive action to prevent harm to U.S. workers and industry, as well as modernized trade authorities that account for NMPP’s continued effects on global supply chains. This work has included raising tariffs on a select number of key sectors to safeguard U.S. supply chains in the face of unfair competition. These tariff modifications will protect historic domestic investments under BIL, the CHIPS and Science Act, and the Inflation Reduction Act, while also shielding American businesses and workers from unfair trade practices.
The Review builds on comprehensive efforts undertaken by the Administration over the last four years, including President Biden’s 2021 Executive Order on America’s Supply Chains (E.O. 14017), which directed rapid supply chain assessments for four critical products in the first 100 days of the Administration, a one-year review of six key supply chains in 2022, and the establishment of the White House Council on Supply Chain Resilience to support the enduring resilience of America’s critical supply chains in 2023.
Additional Actions to Strengthen Supply Chains
Continuing to strengthen supply chains over the next four years—and beyond—will require the United States to deliver on historic domestic investments, maintain and strengthen international partnerships, harness innovation to tackle 21st-century challenges, and mobilize and facilitate ongoing private investment and public-private partnerships. The work of the last four years has laid a strong foundation for the United States to continue safeguarding the enduring resilience of our supply chains for years to come, including for emerging industries of the future.
Below are additional steps the Biden-Harris Administration is taking to strengthen supply chains, including for energy, critical minerals, agricultural commodities and food products, medical products, information and communications technology, transportation, and defense.
Energy
- Announcing up to $6 billion in incentives to strengthen U.S. energy supply chains. Over the coming weeks, the IRS, supported by the Department of Energy’s Office of Manufacturing and Energy Supply Chains (MESC), is set to announce up to $6 billion in additional tax credits to strengthen U.S. energy supply chains through the Qualifying Advanced Energy Project Credit (48C) Program. This builds on the first round of $4 billion in announced tax credits for over 100 projects in 35 states to accelerate domestic clean energy manufacturing and reduce greenhouse gas emissions at industrial facilities. This also builds on over $12 billion of investment from the DOE MESC Office in domestic manufacturing capacity to strengthen the U.S. energy supply chains.
- Improving risk mitigation across the energy supply chain. To improve visibility across multiple technologies in the energy industrial base, DOE and a consortium of the National Laboratories have developed a new analytic framework—the Supply Chain Readiness Level—to quantify risks, gaps, and vulnerabilities, and to identify investment opportunities across the energy sector.
Critical Minerals
- Mapping America’s critical minerals deposits. The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) is announcing new airborne geophysical mapping in the Ozarks Plateau (Missouri, Kansas, and Arkansas) and Alaska over areas known to host minerals such as antimony, tin, tungsten, and lead and zinc ores, as well as byproduct critical minerals such as gallium and germanium. USGS’s mapping work, funded by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL), is revolutionizing the U.S. Government’s understanding of the nation’s mineral and geologic resources. USGS and NASA are partnering to complete the largest high-quality hyperspectral survey in the world, surveying more than 180,000 square miles of the Southwest with sensors that make it possible to “see” nuanced differences between materials.
- Updating the U.S.’s critical minerals market data. Next month, USGS will publish its 2025 Mineral Commodity Summaries. These annual reports help forecast supply chain disruptions resulting from a variety of risks including pandemics, natural disasters, and trade wars, and are the U.S.’s authoritative source of data on the supply, demand, and consumption of 100 mineral commodities. Additionally, last month, researchers at the USGS National Minerals Information Center developed a new model to assess how disruptions of critical mineral supplies may affect the U.S. economy. This model reflects the latest whole-of-government risk and resilience methodology.
Food and Agriculture
- Making $116 million in new investments to expand domestic fertilizer production. Today, the Department of Agriculture (USDA) is announcing eight new awards through its Fertilizer Production Expansion Program, part of a broader effort to increase American-made fertilizer production to spur competition and combat price hikes on U.S. farmers. Since President Biden announced the program in 2022, USDA has invested $517 million in 76 fertilizer production facilities to expand access to domestic fertilizer options for American farmers in 34 states and Puerto Rico. These investments will increase U.S. fertilizer production by 11.8 million tons annually and create more than 1,300 jobs in rural communities. This funding builds on the more than $1.4 billion USDA has invested to build or expand small and medium sized processing facilities and to create a more resilient U.S. food supply chain which gives farmers more market options while providing consumers with more choices and affordable grocery prices.
Medical Products
- Investing an additional $26 million in domestic sterilization capacity. Building on recent investments in industrial base capability and capacity expansion through DPA Title III authorities and Public-Private Partnerships, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) expects additional investments of $26 million in alternative sterilization capacity before the end of 2024.
- Releasing an action plan for the next four years. HHS will publish its Draft 2025-2028 Action Plan for Addressing Shortages of Medical Products and Strengthening the Resilience of Medical Product Supply Chains, outlining supply chain resilience goals and a strategic plan to achieve them. The HHS Action Plan will also include an HHS Research Plan to collate HHS and academic research priorities that would promote Action Plan goals.
- Issuing stronger supply chain standards for hospitals to combat drug shortages. In notice and comment rulemaking, CMS intends to propose new Conditions of Participation requiring hospitals to have certain processes to address and prevent medication shortages.
Semiconductors and Other Technologies
- Investing in domestic production. CHIPS for America has awarded over $26 billion in incentives to advance domestic production in semiconductors and the supply chain. Now, America is home to all five of the world’s leading-edge logic and memory providers, while no other economy has more than two. Since the beginning of the Biden-Harris Administration, semiconductor and electronics companies have announced nearly $450 billion in private investments, catalyzed in large part by public investment.
- Reducing national security risks in federal supply chains. The Department of Defense, General Services Administration (GSA), and National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) are finalizing a rule implementing Section 5949 of the James M. Inhofe National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2023, which prohibits agencies from procuring or obtaining certain products and services that include semiconductors from entities of concern.
- Promoting the U.S. government’s use of domestically manufactured semiconductors. The Made in America Office and Office of Federal Procurement Policy (OFPP) has released a Request for Information (RFI) to gauge the best ways for government contractors to scale up their use of domestically manufactured chips, particularly for critical infrastructure. Responses solicit commercial ideas from industry that may inform future policymaking in support of the government-wide effort to leverage existing manufacturing capacity.
- Incentivizing supply chain diversity, competition, and transparency. The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is issuing guidance to help the Federal Government—the world’s largest buyer—organize its demand for domestic semiconductors so that agencies can mitigate the risk posed by undue dependence on foreign manufacturing, limited competition, and possible higher manufacturing costs. The effort encourages agencies to develop strategies to dual or multiple source semiconductors, increase transparency for critical infrastructure supply chains, and provide the government’s forecasted demand for the products and services that use these chips.
- Protecting American businesses from unfair trade practices. In May, the President announced increased Section 301 tariffs on semiconductor imports from China, which were finalized by the USTR in September, as part of the Biden-Harris Administration’s efforts to further protect American semiconductor manufacturing and the sustainability of domestic investments.
Transportation
- Helping states improve their supply chain operations. The Department of Transportation (DOT) continues to advance this work by working closely with other levels of government and industry stakeholders. DOT’s Freight Office is establishing the National Multimodal Freight Network to assist States in strategically directing resources toward improved system performance for the efficient movement of freight on the Network, to inform freight transportation planning, and to assist in the prioritization of Federal investment.
- Expanding visibility into ocean freight supply chains. Today, DOT is announcing that it has added more members to the Freight Logistics Optimization Works (FLOW) program, a public-private partnership to build an integrated view of U.S. supply chain conditions, and which supported the response to the Francis Scott Key Bridge collapse. Today, FLOW now includes eight of the largest ten container ports representing over 80% of all U.S. imports; nine of the largest ten ocean carriers representing over 70% of all U.S. imports; and six of the largest ten importers.
- Building the transportation of tomorrow. USTDA, DFC, and EXIM are all making investments to improve transportation across air, land, and sea. EXIM’s investments will expand U.S. exports of all electric-powered aircraft, while USTDA is improving the efficiency and safety of freight rail and digital customs processes. In areas around the world with high vessel traffic, DFC is also developing new ports to move goods in critical supply chains from place to place. Since its creation, DFC investments in critical infrastructure have transported over 64 million passengers alone.
Defense
- Releasing a National Defense Industrial Strategy and Implementation Plan. This fall, the Department of Defense (DoD) released the Implementation Plan to accompany its first-ever National Defense Industrial Strategy (NDIS). The NDIS is guiding investments to strengthen supply chain resilience, including by purchasing key elements that we need for sustainable defense production. For example, the United States has invested $215 million to boost production of solid rocket motors, which are one of the most critical components used in our advanced missile systems.
- Establishing domestic manufacturing capability for strategic and critical materials. From mid-2023 through September 2024, DoD invested $250 million in defense-critical materials such as graphite, lithium, niobium oxide, and manganese. These investments will ensure secure access to sources and to domestic separation and processing in support of a range of defense applications, from large-capacity batteries to advanced aircraft to microelectronics.
- Investing in the defense industrial base workforce. The defense supply chain depends in large part on a strong and vibrant workforce. The Administration has pursued numerous initiatives to ensure Americans can access jobs in the defense industrial sector that pay competitive wages and get the training they need to turn these jobs into meaningful careers. Earlier this year, the Navy partnered with the Departments of Education and Labor and with the State of Michigan to launch the Michigan Maritime Manufacturing Initiative, which expands regional training pipelines for the submarine industry into the Great Lakes region.
Strengthening U.S. Government Data, Analytics, and Response Capacity
- Preparing for a second Supply Chain Summit. In September 2024, the Department of Commerce held its first Supply Chain Summit. Commerce convened officials from government, industry, academia, and civil society to discuss how to effectively prepare for and respond to supply chain disruptions, as well as proactively improve supply chain resilience. Commerce will host another Supply Chain Summit in 2025. The Summit will bring together government, industry, and other stakeholders to examine continual progress made in increasing American supply chain resiliency. The date of the Summit will be announced in the months ahead.
- Upgrading the new SCALE diagnostic tool. The Department of Commerce’s Industry and Analysis unit developed a first-of-its-kind supply chain diagnostic tool to assess supply chain risk across the whole of the U.S. economy. The tool proactively helps identify risks and strengthen the resilience of supply chains key to U.S. national and economic security. The Department of Commerce plans to launch a competition aimed at developing new data or analysis that can be used to expand the indicators of risk incorporated into the SCALE tool.
- Conducting supply chain tabletop exercises with industry. In 2025, Commerce will conduct two tabletop exercises with industry to better understand opportunities to address structural supply chain risks faced by the United States. One exercise will focus on supply chain risks in the chemicals industry; the second will focus on an emerging technology where it is critical the United States maintain a strategic advantage.
- Addressing supply chain risks for “critical chemicals.” Working with the interagency, Commerce is developing a list of chemicals that are essential to critical supply chains, and where supply is insecure. Alongside this effort, Commerce is finalizing short-, medium- and long-term policy proposals to strengthen the supply chain. Elements of this work will form the basis of the Chemical Tabletop Exercise in 2025.
Emerging Technologies
- Convening industry on AI data centers. Commerce continues to drive efforts to get ahead of supply chain risks in critical and emerging technologies by developing playbooks and conducting deep dive assessments into emerging technologies such as quantum computing and clean hydrogen. In the second half of 2024, Commerce carried out a sprint to assess under-the-radar risks in AI data center supply chains, engaging more than 35 companies and leveraging in-house industry expertise and the SCALE tool to assess the highest-risk components and identify steps that government and industry can take to address them. In December, Commerce convened companies to share the results of its analysis and identify next steps.
Building Resilience with Allies and Partners
- Presidential Summit on Global Supply Chain Resilience. In October 2021, President Biden convened over a dozen world leaders to improve international collaboration on supply chain resilience. Following the President’s convening, the Secretaries of State and Commerce hosted a Supply Chain Ministerial to further advance this work. The original Joint Statement from the ministerial now has 31 signatories who have agreed to make global supply chains more transparent, diverse, secure, and sustainable.
- Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) Supply Chain Agreement. The IPEF Supply Chain Agreement entered into force in February 2024 and will improve the preparedness, resilience, and competitiveness of regional supply chains. The United States and 13 Indo-Pacific partners have established a Supply Chain Council. In 2025, the Council will develop and implement action plans to strengthen supply chains across several critical industries. A Crisis Response Network will serve as a warning system for potential supply chain disruptions, and a Labor Rights Advisory Board will convene IPEF government officials, employers, and labor officials to improve labor rights and workforce development across regional supply chains.
- Eradicating forced labor from supply chains. As part of the Partnership for Workers’ Rights launched in 2023, the U.S. and Brazil worked with businesses and unions to address worker vulnerability to forced labor in supply chains for cattle, coffee, gold, charcoal, and other goods.
- Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGI). PGI is a bipartisan initiative in partnership with the G7 to provide strategic, values-driven, and high-standard infrastructure and investment in low- and middle-income countries. Through initiatives like the Lobito Trans-Africa Corridor, highlighted on the President’s recent visit to Angola, the United States is working with partners to strengthen and diversify supply chains.
- G7 Surge Financing Initiative. The U.S. International Development Finance Corporation (DFC), G7 development finance institutions (DFIs), European Investment Bank (EIB), International Finance Corporation (IFC), and MedAccess announced the Surge Financing Initiative for Medical Countermeasures (MCMs). Together, partners are working closely with global and regional health organizations to establish frameworks and innovative financing mechanisms to support more rapid and equitable pandemic response.
- Boosting critical mineral capacity with partners. DFC invested over $220m in rare earth, graphite, and nickel projects in the last four years, reducing dependence on strategic adversaries and improving resilience in the critical mineral supply chain. The Department of Labor, USAID, United States Trade and Development Agency (USTDA), and the State Department through the Minerals Security Partnership have also provided technical support to bring new capacity online to process critical minerals in line with international best practices.
- Strengthening resilient telecommunications. In Costa Rica, EXIM approved a preliminary commitment to support Costa Rica’s use of trusted vendors to deploy its 5G network. With Japan and Australia, DFC is supporting the delivery of high-quality telecommunication services for over 2.5 million subscribers across Papua New Guinea, Fiji, Vanuatu, Samoa, Tonga, and Nauru.