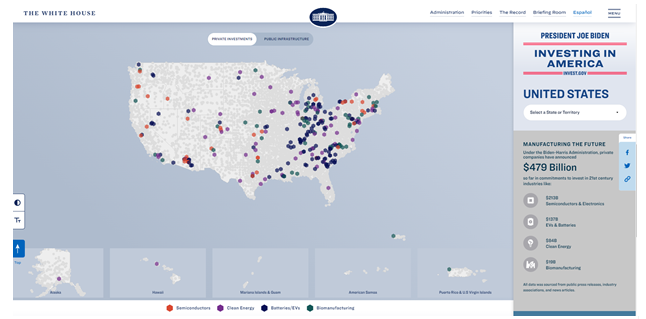
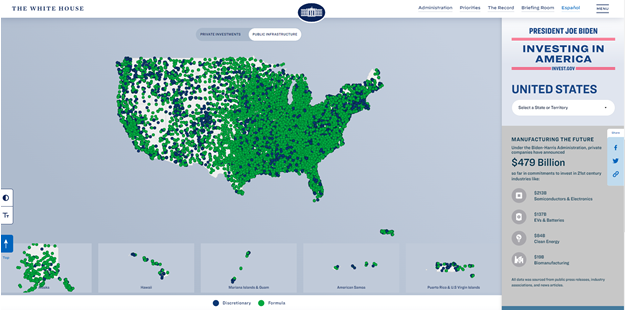
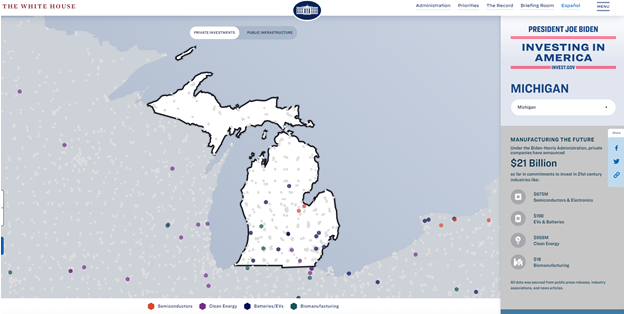
Largest Internet Funding Announcement in History Kicks Off Administration-Wide Investing in America Tour
High-speed internet is no longer a luxury – it is necessary for Americans to do their jobs, to participate equally in school, access health care, and to stay connected with family and friends. Yet, more than 8.5 million households and small businesses are in areas where there is no high-speed internet infrastructure, and millions more struggle with limited or unreliable internet options. Just like Franklin Delano Roosevelt’s Rural Electrification Act brought electricity to nearly every home and farm in America, President Biden and Vice President Harris are delivering on their historic commitment to connect everyone in America to reliable, affordable high-speed internet by the end of the decade.
The Department of Commerce announced funding for each state, territory and the District of Columbia for high-speed internet infrastructure deployment through the Broadband Equity Access and Deployment (BEAD) program—a $42.45 billion grant program created in the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and administered by the Department of Commerce. This announcement—the largest internet funding announcement in history—kicks off the three-week Administration-wide Investing in America tour, where President Biden, Vice President Harris, First Lady Jill Biden, Cabinet members, and Senior Administration Officials will fan out across the country to highlight investments, jobs, and projects made possible by President Biden’s economic agenda.
Among the highlights:
- Awards range from $27 million to over $3.3 Billion, with every state receiving a minimum of $107 million.
- 19 states received allocations over $1 billion with the top 10 allocations in Alabama, California, Georgia, Louisiana, Michigan, Missouri, North Carolina, Texas, Virginia and Washington.
- With these allocations and other Biden administration investments, all 50 states, DC, and the territories now have the resources to connect every resident and small business to reliable, affordable high-speed internet by 2030.
Details related to the BEAD allocation for the states, D.C., and territories, as well as the total Federal investment in high-speed internet in each State and Territory are available here.
In addition to helping connect everyone in America to high-speed internet, this funding will support manufacturing jobs and crowd in private sector investment by using materials Made in America. For example, anticipating this major investment in high-speed internet infrastructure deployment, earlier this year, fiber optic cable manufacturers CommScope and Corning announced $47 million and $500 million expansions of their domestic manufacturing capacity, which will create hundreds of good-paying American jobs in North Carolina. These investments are part of the nearly $500 billion in private sector manufacturing and clean energy investments spurred by the President’s Investing in America agenda. The Investing in America agenda represents the most significant upgrade to our nation’s infrastructure in generations—an investment larger than FDR’s Rural Electrification effort, Eisenhower’s effort to build the Interstate Highway system, and the construction of the Panama Canal.
Internet for All
The announcement of BEAD funds is just one component of the Biden-Harris Administration’s efforts to ensure that everyone in America has access to affordable, reliable high-speed internet as part of President Biden’s Investing in America agenda. In recent weeks, the Administration has announced over $700 million in USDA ReConnect awards, over $900 million in NTIA Middle Mile awards and launched the Online for All campaign to increase ACP enrollment and visibility. Beyond BEAD, billions have already been announced or distributed to all states and territories to build out high-speed internet infrastructure by the Biden-Harris Administration.
In addition to BEAD, the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law includes:
- $14.2 billion for the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP), which provides eligible households up to $30/month (up to $75/month on qualifying Tribal Lands) off their internet bill, as well as a one-time $100 toward a desktop, laptop or tablet computer offered by participating internet service providers. Thanks to commitments by over 20 internet service providers, millions of Americans are using the Affordable Connectivity Program to access internet for free. Today, 19 million Americans are enrolled in this program. Households can check their eligibility and sign up at GetInternet.gov.
- $2.75 billion for the Digital Equity Act, which provides grants to ensure communities have the skills and support needed to take advantage of high-speed internet connections;
- An additional $2 billion for the Tribal Broadband Connectivity Program, which provides grants to federally recognized Tribal governments, Tribal organizations, Tribal Colleges and Universities, the Department of Hawaiian Homelands, and Alaska Native Corporations for high-speed internet deployment on Tribal lands, as well as for telehealth, distance learning, high-speed internet affordability, and digital inclusion;
- $2 billion for the Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) Reconnect Program, which provides loans and grants primarily to build high-speed internet infrastructure in eligible rural areas;
- $1 billion for the Middle Mile Program, which provides funding for the “middle mile” backbone of internet networks.
President Biden’s American Rescue Plan also included over $25 billion for high-speed internet, including:
- The Department of Treasury’s Capital Projects Fund (CPF) provides $10 billion to states, territories, and Tribes for which high-speed internet is an eligible use. Today, over $7 billion has already been dedicated to high-speed internet deployment and connectivity across 45 states;
- The Coronavirus State and Local Fiscal Recovery Funds (SLFRF) delivered funding across the country to support the response to and recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic. About $8 billion is being used by states, territories, Tribes, and local governments for high-speed internet deployment and connectivity; and,
- The Federal Communications Commission’s (FCC) $7 billion Emergency Connectivity Fund program helped schools and libraries close the “homework gap,” providing schools and libraries with 10.5 million connected devices and over 5 million internet connections.
Additional information on Biden-Harris high-speed internet programs and funding is available at InternetForAll.Gov.
GOVERNOR HOCHUL, SENATOR SCHUMER, SENATOR GILLIBRAND AND NEW YORK CONGRESSIONAL DELEGATION ANNOUNCE NEW YORK WILL RECEIVE MORE THAN $664 MILLION IN FEDERAL BROADBAND EQUITY, ACCESS, AND DEPLOYMENT FUNDS
Governor Kathy Hochul, Senator Schumer, Senator Gillibrand and the New York Congressional Delegation today announced New York State’s ConnectALL Office has been allocated more than $664 million in funding from the federal Broadband Equity Access and Deployment Program, part of the 2021 Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. The BEAD allocation is the largest single investment in the ConnectALL program and will be used primarily for providing fiber optic infrastructure to locations in New York that currently have no broadband service.
“This transformative investment in New York’s ConnectALL program will be a gamechanger in advancing our statewide strategy to make affordable, high-speed internet available to all,” Governor Hochul said. “In today’s economy, reliable broadband access is an absolute necessity, and I thank the Biden administration, Majority Leader Schumer, Senator Gillibrand, and New York’s congressional delegation for continuing to prioritize critical infrastructure needs and for supporting our mission to expand broadband to every corner of our state.”
The $1+ billion ConnectALL initiative, announced by Governor Hochul in her January 2022 State of the State Address, is New York State’s largest-ever public investment in broadband, aimed at transforming the state’s digital infrastructure to connect all New Yorkers to the internet. In addition to funding to reach unserved and underserved locations, ConnectALL includes grant programs to invest in public broadband infrastructure, to upgrade service to affordable and public housing, and to support digital inclusion and education on using the internet.
New York will submit an initial grant distribution proposal to President Biden’s National Telecommunication and Information Administration (NTIA). Following approval of the initial proposal, the ConnectALL Office will solicit applications from internet service providers to build new broadband infrastructure in unserved and underserved areas of the state. That package of applications will be included in New York’s final proposal to NTIA, after which the state will receive its full BEAD allocation to issue grant awards.
The BEAD allocation follows a $100 million award from the Treasury Department’s Coronavirus Capital Projects Fund announced by the Governor in May and two planning grants totaling over $7 million announced in December.
The BEAD allocation is based largely on New York’s portion of the nation’s unserved locations, as reported by the Federal Communications Commission. The FCC’s map originally showed New York had 106,290 unserved locations. In October 2022, Governor Hochul issued a challenge to the FCC’s broadband data maps, which revealed more than 31,000 underserved and unserved locations missing from the FCC’s data, following a statewide mobilization of regional, county, and local officials and New York’s own, first-of-its-kind interactive broadband map. In May, the FCC released updated data including over 140,000 unserved locations in New York and nearly 38,000 locations that have access to the minimal level of internet speeds to qualify as underserved.
US Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo said,”Through President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, we are making the largest investment ever to deliver reliable and affordable high-speed Internet for all New Yorkers, close the digital divide in the Empire State, and create thousands of good jobs as we build out our network infrastructure. I appreciate Governor Hochul’s leadership and work to ensure New York families will be able to connect to the digital economy and access even more opportunities to learn, work, and grow.”
Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer said, “Thanks to the Bipartisan Infrastructure & Jobs Law we passed, a historic nearly $670 million is now on its way to expand broadband infrastructure and boost high-quality internet access across New York. Whether it is for work, school, or getting the healthcare you need, access to the internet is not luxury, but a necessity for modern life. Long before the pandemic, communities across New York, from rural communities Upstate to bustling city neighborhoods, have struggled to obtain reliable high-speed internet service. I am proud to deliver this record setting nearly $670 million for New York to help finally close the digital divide. New York, under Governor Hochul’s leadership, is leading the charge to get all New Yorkers the equitable access to the internet they deserve, and this major federal investment will help finally give our communities the support they need to succeed in the 21st century.”
Senator Kirsten Gillibrand said, “Access to affordable, high-quality internet is critical to connect New Yorkers with work, health care, education and more. This funding will go directly toward bridging the digital divide and deliver high-speed internet to families across New York State. I am proud to have worked to deliver this funding through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and I will continue to fight so every New Yorker has access to reliable, high-quality internet.”
Democratic Leader Hakeem Jeffries said, “In New York and throughout America, there are far too many under-resourced communities without the ability to connect online and engage with family, work, school and telemedicine. Working with President Biden, House Democrats passed the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act to ensure that every single community throughout our nation has access to high-speed internet. We invested $65 billion to expand broadband in every single zip code. I thank President Biden and Governor Hochul for their leadership in shepherding $665 million in crucial investments across New York.”
Representative Grace Meng said, “In Congress, I’m proud to have helped create the $7.1 billion Emergency Connectivity Fund, which helped schools and libraries in Queens and across New York purchase Wi-Fi hotspots, modems, routers, internet service and internet-enabled devices so that we could increase access to the internet in our communities. I thrilled to hail this BEAD allocation as well, and glad to see that the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law that I helped pass continues to deliver for our state. I will continue championing the crucial issue of improving internet and broadband access, and I thank Governor Hochul for announcing these funds.”
Representative Richie Torres said, “Reliable, accessible, and quality internet access is no longer a luxury — it is a necessity for almost every aspect of everyday life. That’s one reason why I was proud to support the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, which continues to deliver historic and critical investments in New York and across America. Too many of our communities have historically been left behind without the ability to easily get online and be connected. But with this funding, our state and federal governments will work together to deploy broadband service equitably to make sure every New Yorker has the internet service they need and deserve.”
Other ConnectALL Initiatives
Under Governor Hochul’s leadership, the ConnectALL Office is gathering an unprecedented level of community input to inform its broadband work. ConnectALL recently completed a three-month, statewide tour of 10 digital equity listening sessions to inform the development of the BEAD Five-Year Action Plan, the BEAD Initial Proposal, and the State Digital Equity Plan. ConnectALL will continue to meet with community stakeholders, coalitions, and statewide networks, including through the New York State Internet Access Survey, which closes on June 30. ConnectALL will make the New York State Digital Equity Plan available for public comment in September.
In addition, New York State continues to drive nation-leading enrollment in the federal Affordable Connectivity Program, a nationwide subsidy to expand broadband access to low-income households. New York has enrolled more than 1.3 million households in the program as a result of a multi-agency, multi-pronged outreach effort led by the New York State Department of Public Service and Empire State Development.